chemistry
Chemistry is a branch of science that deals with the study of the composition, properties, and behavior of matter, as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions. It is often called the central science because it connects the physical and biological sciences. Chemistry is a fundamental science that explains how substances interact with one another and how they are transformed into new substances.
Chemists study matter at the atomic and molecular levels, which involves understanding the nature of atoms, ions, molecules, and the forces that act on them. They investigate the structure of substances, the ways in which they interact, and the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions. Chemistry also deals with the properties of different substances, such as their physical and chemical properties, and how these properties can be used to identify and classify substances.
Chemistry is used in many different fields, including medicine, engineering, agriculture, and environmental science. It plays a crucial role in developing new materials, pharmaceuticals, and technologies, and it helps us understand the natural world and the processes that govern it.
Table of Contents
Finkelstein Reaction
This reaction used for the preparation of the alkyl iodides
the finkelstein reaction is
NaI is precipitate form. that’s why reaction will R-I
NaI is more covalent and soluble in acetone
and NaBr and NaCl is ionic compounds and are insoluble and it form ppt
Elements and its atomic Number , Atomic mass and symbol
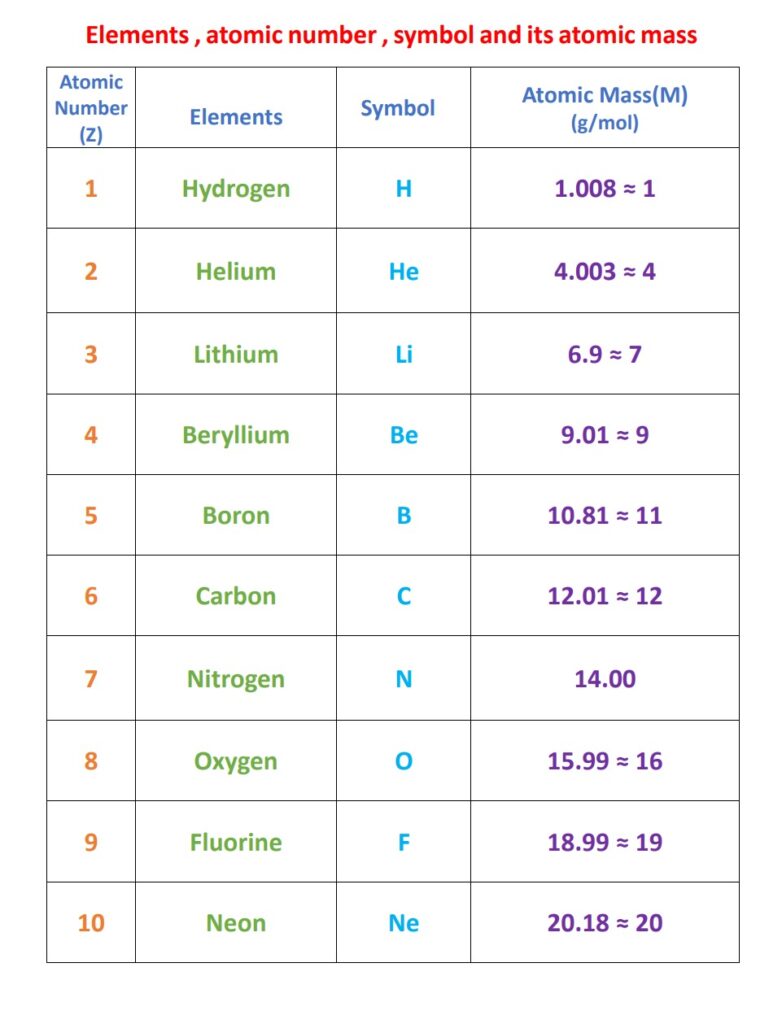

The Atomic Number and Its Formula
When it comes to understanding the structure and properties of atoms, one fundamental concept that plays a crucial role is the atomic number. In this article, we will delve into what the atomic number is, how it is determined, and its significance in the world of chemistry.
What is the Atomic Number?
The atomic number of an element is a unique identifier that represents the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. It is denoted by the symbol “Z” and is one of the key characteristics used to classify and organize elements on the periodic table.
Each element on the periodic table has a distinct atomic number. For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, indicating that it has one proton in its nucleus. Carbon, on the other hand, has an atomic number of 6, indicating that it has six protons.
How is the Atomic Number Determined?
The atomic number is determined by the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. Since protons have a positive charge, they are balanced by an equal number of negatively charged electrons orbiting around the nucleus, creating a neutral charge for the atom as a whole.
Scientists have conducted extensive experiments and observations to determine the atomic numbers of different elements. One of the most significant breakthroughs in this area was the work of Henry Moseley in the early 20th century. Moseley’s experiments with X-rays led to the discovery that the atomic number of an element is directly related to the frequency of X-rays emitted when atoms are bombarded with electrons.
Today, the atomic number of each element is known with great precision and is an essential piece of information used in various scientific calculations and applications.
The Formula for Atomic Number
The formula for calculating the atomic number of an element is quite simple:
Atomic Number (Z) = Number of Protons
As mentioned earlier, the atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom. Since the number of protons determines the element’s identity, the atomic number is often used to identify and classify elements.
It is important to note that the atomic number remains constant for a specific element, regardless of the number of neutrons or electrons it may have. Isotopes, which are variants of an element with different numbers of neutrons, will have the same atomic number but different atomic masses.
Significance of the Atomic Number
The atomic number is of paramount importance in chemistry and physics. It provides valuable information about an element’s properties, including its chemical behavior, atomic mass, and electron configuration.
The atomic number also determines an element’s position on the periodic table. Elements are arranged in ascending order of atomic number, which allows scientists to group elements with similar properties together. This organization provides a systematic way to study and understand the behavior of different elements and their compounds.
Additionally, the atomic number plays a crucial role in balancing chemical equations. It helps determine the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an atom, which is essential for predicting and explaining chemical reactions.
In conclusion, the atomic number is a fundamental concept in the world of chemistry. It represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus and serves as a unique identifier for each element. Understanding the atomic number and its formula is key to comprehending the properties and behavior of elements and their compounds.
The definition of Arrhenius base is
- the compound that contains hydroxide and dissolve in water to form OH^-
- a compound that is proton donor
- a compound that is proton accepter
- a compound that contains a hydrogen atom and dissolve in water to form a hydrogen ions H^+
Ans :-
- the compound that contains hydroxide and dissolve in water to form OH^-
if you want to study mathematic , physics and English you can visit our your channel @akroyclasses.